고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
데이터 과학에서는 일반적으로 히스토그램, 히트 맵과 같은 그래프들과 플롯, 평균, 중앙값, 모드, 확률, 분산 등과 같은 수학적 계산이 많이 사용되는데, 이러한 데이터들을 계산하기에 앞서, 정리할때 가장 많이 사용되는 파일 형식은 xls, xlsx, csv, txt 등이 있습니다.
사실 Python 프로그래밍 언어가 데이터 과학 분야에서 사용되는 것으로 잘 알려져 이유가 바로, 이러한 파일들에 대한 조작이 매우 쉽게 잘 정리되기 때문이라고 볼 수 있습니다.
그래서 이번 강좌는 우리가 흔히 사용하는 Excel 파일을 읽을 수 있는 파이썬의 두가지 방법을 소개하고자 합니다.
0. 예제 엑셀파일
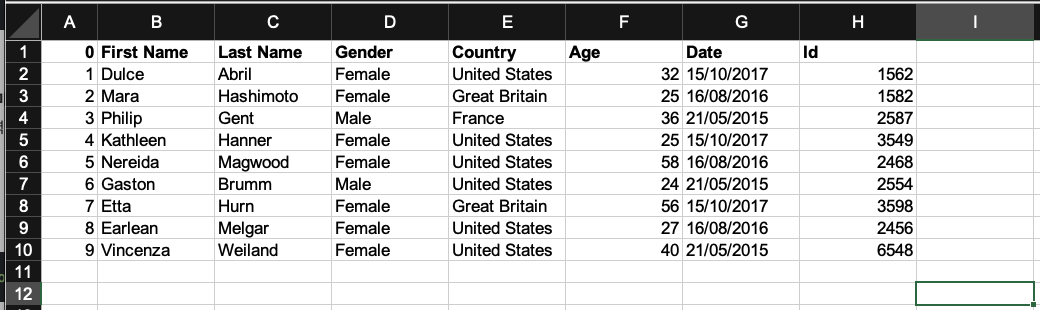
다운로드
1. pandas 패키지를 사용하여 Excel 파일 읽기
Python에서는 pandas 라이브러리를 사용하여 Excel 파일을 읽을 수 있습니다. pandas 모듈은 Python으로 작성된 강력하고 강력하며 빠르고 유연한 오픈 소스 데이터 분석 및 조작 라이브러리입니다.
pandas 라이브러리 설치는 다음과 같습니다.
pip install pandas
- pandas 모듈을 사용하여 Excel 파일을 읽는 기본 방법은 다음 코드와 같습니다.
import pandas
df = pandas.read_excel("samples.xls")
print(df)출력:

- 특정 시트(sheet)를 지정하는 경우
import pandas as pd
df = pd.read_excel("samples.xls", sheet_name='Sheet1')
print(df)출력:

- 엑셀 데이터의 header를 지정하는 방법
pd.read_excel('samples.xls, header = 1)출력:

- 엑셀데이터의 col 인덱스를 지정하는 방법
출력:

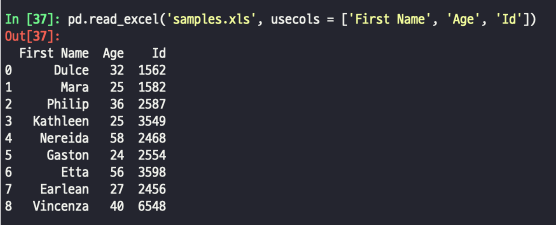
- 불러올 열을 지정하는 방법
pd.read_excel('samples.xls', usecols = ['First Name', 'Age', 'Id'])출력:

- 특정 열값을 불러오기
import pandas
df = pandas.read_excel("samples.xls")
column = df.columns[4]
print(column)
print("-" * len(column))
for index, row in df.iterrows():
print(row[column])출력:

- 블러올 행을 지정하는 방법
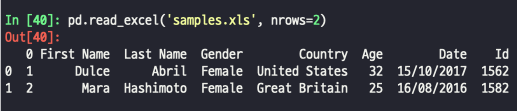
- nrows : 불러올 행 개수 제한 / 처음 ~ n번째 행만 불러오기
- skiprows : 처음 ~ n번째 행 제외 / n+1번째 ~ 마지막까지
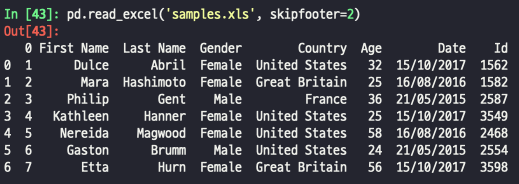
- skipfooter : 뒤에서 n개 제외
# 앞에서 n개 행 생략
pd.read_excel('파일명.xlsx', skiprows = n)
# 처음 ~ n번째
pd.read_excel('파일명.xlsx', nrows = n)
# 뒤에서 n개 행 생략
pd.read_excel('example.xlsx', skipfooter = n)출력:

2. xlrd 패키지를 사용하여 Excel 파일 읽기
Python에서는 xlrd 패키지를 사용하여 Excel 파일을 읽을 수 있습니다. xlrd 모듈은 Excel 파일을 읽고 서식을 지정하는 데 사용되는 Python 패키지입니다. 컴퓨터 또는 가상 환경에 설치되어 있지 않은 경우 다음 명령을 사용합니다.
- xlrd를 설치하려면 다음 명령을 사용하십시오.
pip install xlrd
xlrd를 사용하여 Excel 파일을 읽는 방법은 다음 코드를 참조하십시오.
from xlrd import open_workbook
wb = open_workbook('samples.xls')
sheet = wb.sheet_by_index(0)
sheet.cell_value(0, 0)
columns = []
for i in range(sheet.ncols):
columns.append(sheet.cell_value(0, i))
print(columns)출력:

- 데이터 csv 형식으로 불러오기
from xlrd import open_workbook
wb = open_workbook('sample.xls')
sheet = wb.sheet_by_index(0)
sheet.cell_value(0, 0)
count = 3
for i in range(1, count + 1):
for j in range(sheet.ncols):
print(sheet.cell_value(i, j), end = ", ")
print()
출력:

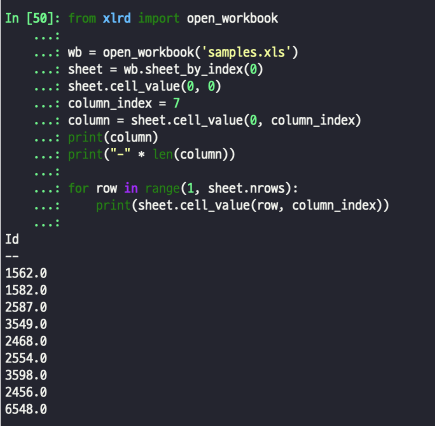
- 특정 열값 불러오기
from xlrd import open_workbook
wb = open_workbook('samples.xls')
sheet = wb.sheet_by_index(0)
sheet.cell_value(0, 0)
column_index = 3
column = sheet.cell_value(0, column_index)
print(column)
print("-" * len(column))
for row in range(1, sheet.nrows):
print(sheet.cell_value(row, column_index))출력:
'멘토링' 카테고리의 다른 글
| UML 다이어그램 종류와 분류 (1) | 2022.07.15 |
|---|---|
| 레거시 vs 버츄얼 머신 vs 컨테이너기반시스템 (0) | 2022.07.13 |
| [mac os] m1 맥미니 selenium 크롤링 개발환경 (0) | 2022.04.09 |
| 자바스크립트의 MutationOberver 에 대하여.. (0) | 2022.03.31 |
| Git 초보분들을 위한 입문자료 (0) | 2022.03.29 |





댓글 영역